Date
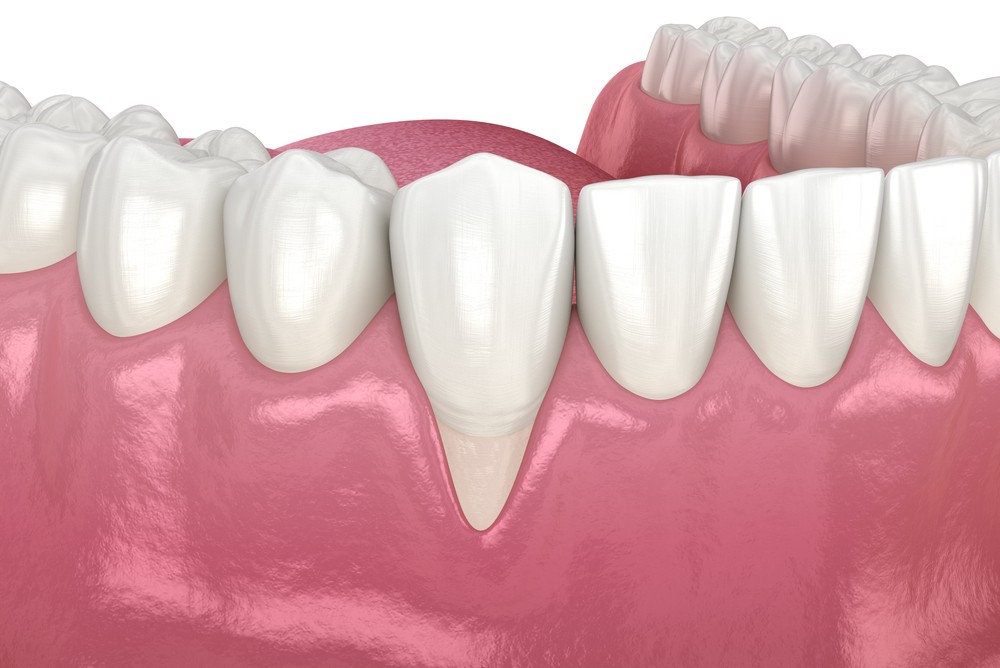
Gum recession is one of many issues your dentist can detect during a routine visit. In healthy teeth, firm gum tissue surrounds the base of teeth and covers their roots. The tissue acts as a protective barrier to prevent harmful bacteria from reaching the roots and jawbone.
When gums recede, however, the gum tissue starts to pull away from the teeth, uncovering more of the affected tooth over time and exposing the tooth’s roots. Bacteria can easily collect in pockets that form between the teeth and gumline. Untreated, this leads to periodontal disease and even bone or tooth loss.
While gum recession is a common issue, most people don’t realize that their gums are receding until the condition reaches advanced stages. Left unchecked, receding gums can lead to many undesirable symptoms including one or more of the following:
- Gums that bleed easily, especially after brushing and flossing
- Foul-smelling breath
- Pain, redness and inflammation in the gums
- Loose teeth
- Increased sensitivity to hot or cold foods
- A tooth or teeth that appear much longer than normal
What Causes Gum Recession?
There are many causes of gum disease. Some causes are preventable, while others can be extremely difficult to control. If you think your gums are receding, schedule a visit with your dentist right away for effective treatment.
The most common causes of gum recession include:
- Periodontal disease: Gum disease is a major cause of receding gums. Harmful bacteria infect the bones that anchor your teeth in place and can cause gum tissue to detach from teeth.
- Vigorous toothbrushing: Brushing your teeth too hard or brushing with a hard-bristled toothbrush can erode the tooth enamel and irritate your gum tissue.
- Hormonal changes: Hormonal changes that women experience during puberty, pregnancy and menopause can make gums more sensitive and increase the risk for developing gum disease and gum recession.
- Grinding teeth: Chronic clenching or grinding your teeth exerts too much force on the teeth, causing gums to recede over time.
- Genetics: If one or both of your parents have receding gums, you may be at a greater risk for gum recession as well.
- Poor dental health: Without proper brushing and flossing, plaque builds between the teeth and gums. The harmful bacteria in plaque can destroy surrounding gum tissue and supporting bone structure.
What Is Treatment for Receding Gums?
Unfortunately, if your gums have already started to pull away, it cannot be reversed. If your case is mild, simply improving your oral hygiene habits and monitoring the condition with the help of your dentist is the best way to stop the progression.
For more severe forms of receding gums, your dentist may perform a deep cleaning of the affected area to remove plaque and tartar. In extreme cases, surgery to treat gum recession may be required, due to excess bone loss and deep pockets in the gum tissue.
We are able to track recession between visits with our digital health scan. The best way to prevent gum recession is to take good care of your mouth through regular brushing, daily flossing, good eating habits and routine checkups with your dentist. Most importantly, seek treatment immediately if you notice any signs of gum recession to prevent the situation from getting worse.


 703-734-2750
703-734-2750